Shallow Copy
When you shallow copy an object there is no new memory space that is allocated to the duplicate object. Thus both original and duplicate object shares the same memory space.
As a result of this, changing the attributes in one object changes the attribute in the other. Below is an example of a Shallow copy in JS.
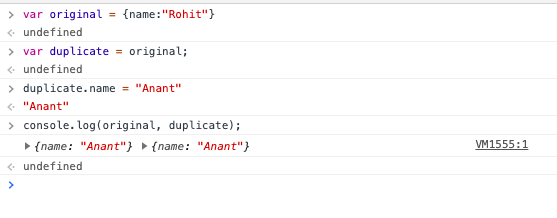
If you see the output above you will notice that we modified the attribute name of the duplicate object and the change got replicated in the original object as well.
This happened since both the objects share the same memory and when we modified the value on one object it changed the shared memory. Note that variables are just references to the memory space.
// Shallow Copy
var original = {name:"Rohit"}
var duplicate = original;
duplicate.name = "Anant";
console.log(original, duplicate);
//{name: "Anant"}, {name: "Anant"}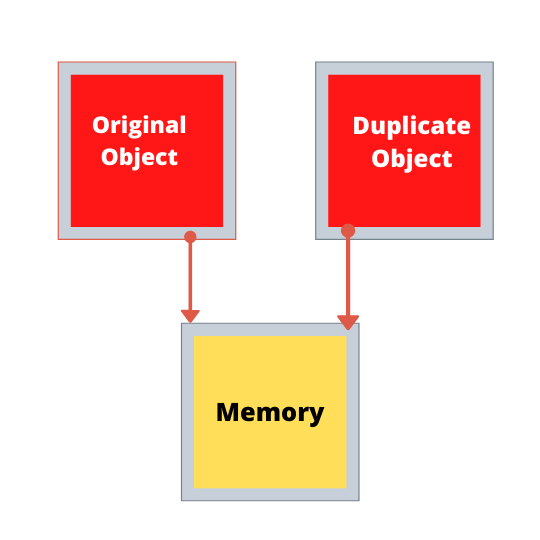
Deep Copy
In contrast to Shallow copy, Deep copy allocates new memory for the duplicate object. So now when you change attributes in one object it doesn’t affect the other object and all this achieved by the spread operator.
Spread operator syntax: {…variableToBeCopied}
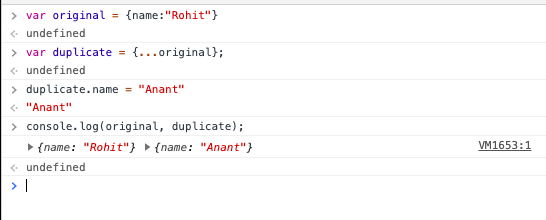
Unlike previous example of shallow copy you would now see that the value of original has not changed after changing the value of duplicate object.
// Deep Copy
var original = {name:"Rohit"}
var duplicate = {...original};
duplicate.name = "Anant";
console.log(original, duplicate);
//{name: "Rohit"}, {name: "Anant"}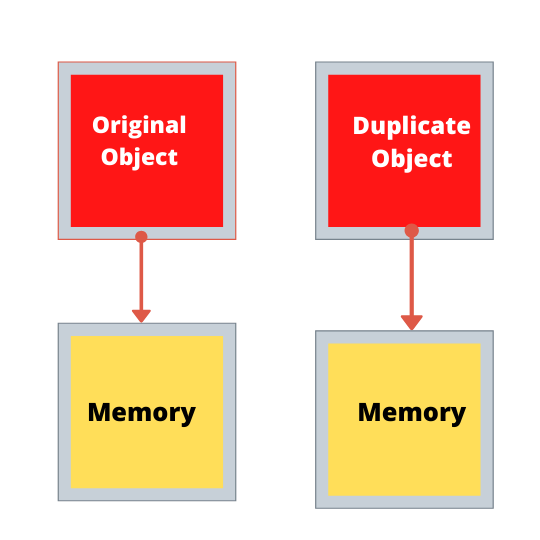
Deep Copying using Object object 🙂
Object.assign(copyTo, copyFrom) can be used to create deep copy of an object. Below is the code for the same.
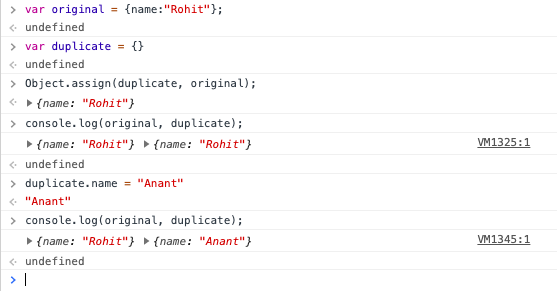
var original = {name:"Rohit"}
var duplicate = {};
Object.assign(duplicate,original)
duplicate.name = "Anant";
console.log(original, duplicate);
//{name: "Rohit"}, {name: "Anant"}Hope this post was helpful in understand Shallow Copy and Deep Copy in JavaScript.
Happy Coding !!
