Execution Context and Call Stack are important concepts in JS, which if you understand properly would help you make peace with Closure and digest Hoisting. On a separate note, Execution Context is the basis of most of the interview questions.
Call Stack
The global function in JS is an anonymous function that defines and calls its self. Once called it is added as an anonymous function at the bottom of the call stack. As the global function executes any function calls made are added on top of the call stack and JS being single-threaded finishes the topmost function execution and then returns to the underneath function.
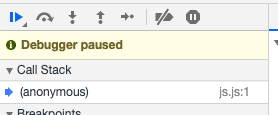
Below is an example of the same.
var a = 10;
function aho(){
var a = 20
function aikla(){
console.log(a)
}
aikla();
}
aho();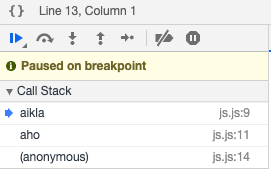
Execution Context
Execution Context simply is an abstract concept of an environment where the Javascript code is evaluated and executed. Execution Context has two phases i.e creation phase and execution phase.
In the creation phase variables and functions are allocated memory. Variables are assigned default value i.e undefined and functions are simply assigned with function reference.
In the next phase, i.e execution phase code is actually executed and values are assigned to variables, and function calls are executed.
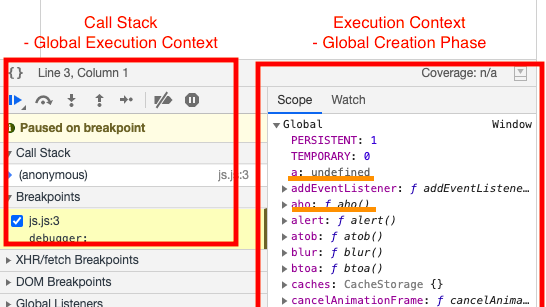
Global Execution Context
var a = 10;
function aho(){
var a = 20
console.log(a)
}
aho();If we consider the above code, the Global function i.e anonymous function when executes creates a Global Execution Context and adds to the call stack as explained above. Like any EC GEC goes through the creation and execution phase.
In the creation phase variable, a is assigned value undefined it’s only during the execution phase variable a is assigned with the actual value i.e 10. Likewise for function call aho() is assigned with reference to the function aho
Function Execution Context
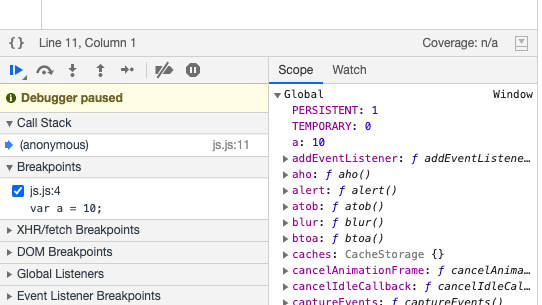
Now here is the important part functions in JS are treated as new code, i.e functions have their own Execution Context and are pushed on top of Call Stack when a function call is made.
In our example when a function call is made control flows to line 6 and a new Function Execution Context is added on top of Call Stack as shown in the below image.
FEC goes through creation and execution phase as demonstarted in below images.
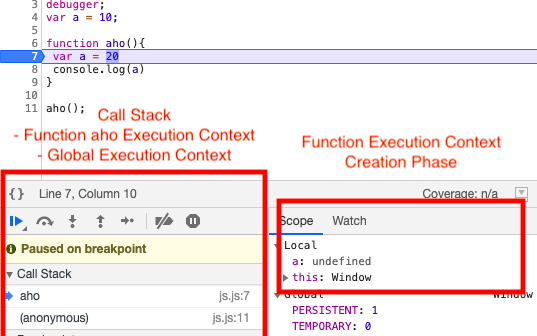
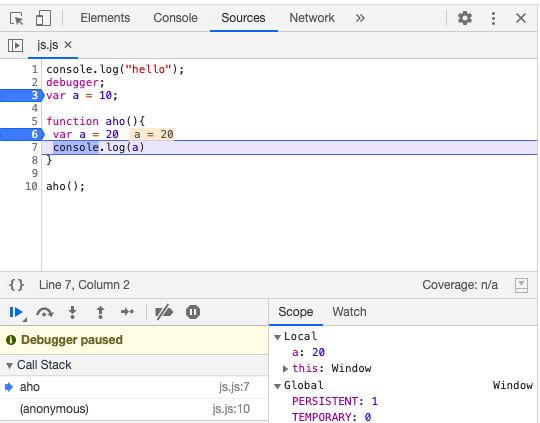
Once the execution of the function aho is complete it is removed from Call Stack and memory is deallocated as shown below.
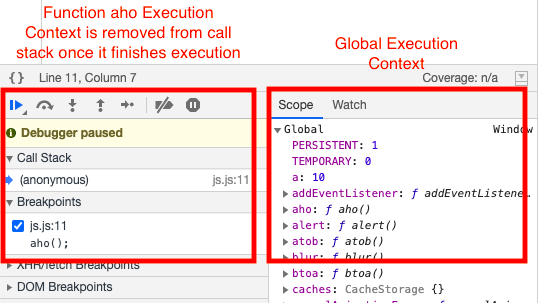
Control then flows back to Global Execution Context and execution continues until the end of the program once the execution is finished even the Global Execution context is removed from Call Stack thus making Call Stack empty as can be seen in the below image.
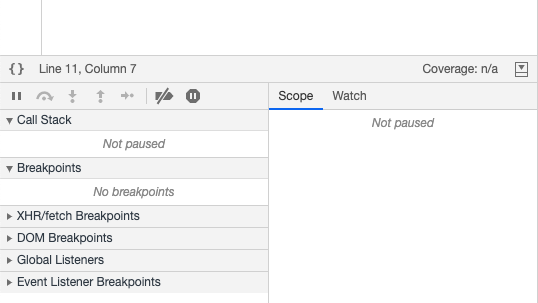
Hope this was helpful, Happy coding.
